Thondar Newsroom
The first session of the 2025 MRT (Multispectral Refraction Topography) Lecture has officially opened. Professor Yu Zhang from Peking University Third Hospital delivered a keynote presentation entitled "The Code of the Relationship Between Myopia Control with Orthokeratology Lenses and Peripheral Retinal Defocus."
Based on clinical data, the presentation analyzes the defocus mechanism of orthokeratology (OK) lenses and explores the integrated application of MRT technology. The analysis clarifies the intersection of the two technologies and provides academic references for advancing the precision of myopia management.
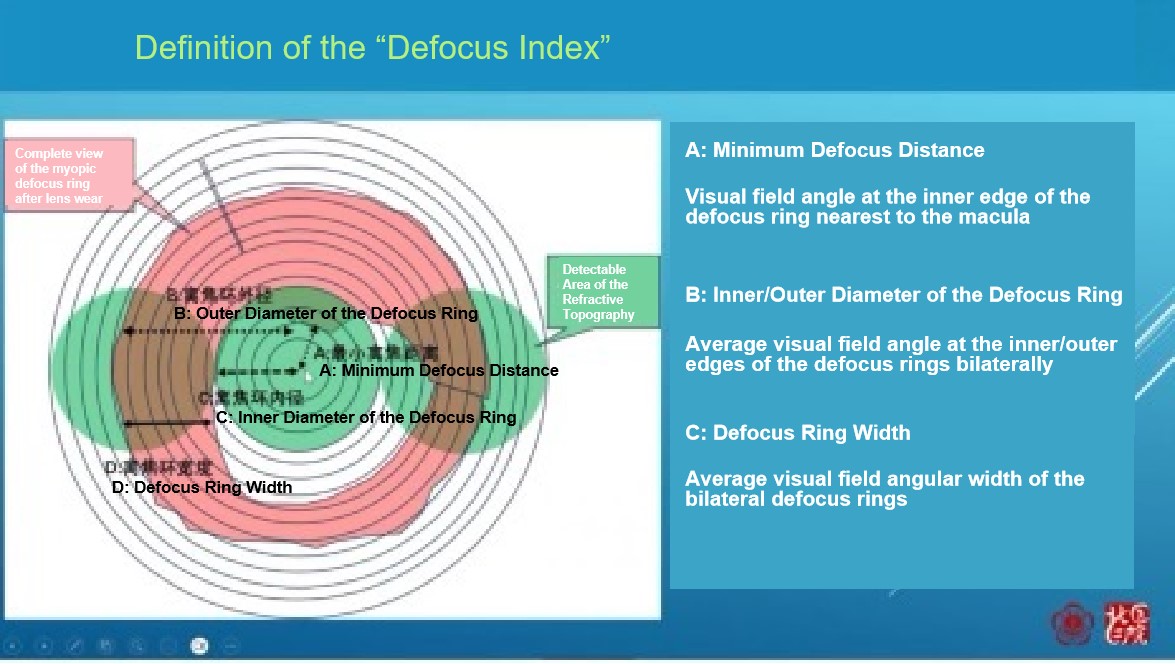
Professor Yu Zhang noted that the core mechanism underlying myopia control with orthokeratology (OK) lenses lies in the defocus ring they form. By reshaping corneal morphology, OK lenses create a myopic defocus ring, which inhibits axial elongation through myopic defocus signals. The key determinants of this mechanism are the position, width, and magnitude of the defocus ring. Research has confirmed that within a certain range, the closer the defocus ring is to the macula, the greater its width, and the higher the defocus magnitude, the more significant the myopia control effect.
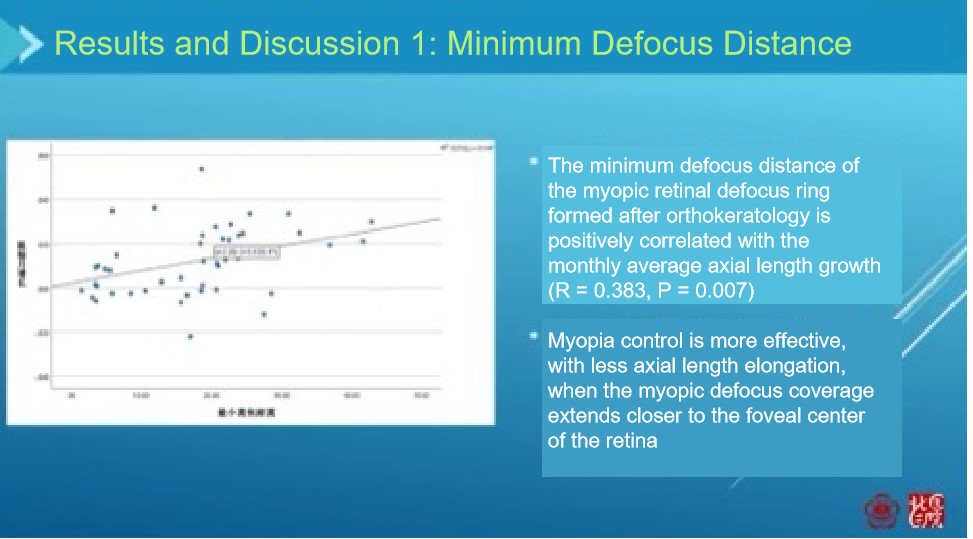
There is a positive correlation between the minimum defocus distance and axial elongation (within a certain range, the smaller the minimum defocus distance, the slower the axial elongation).
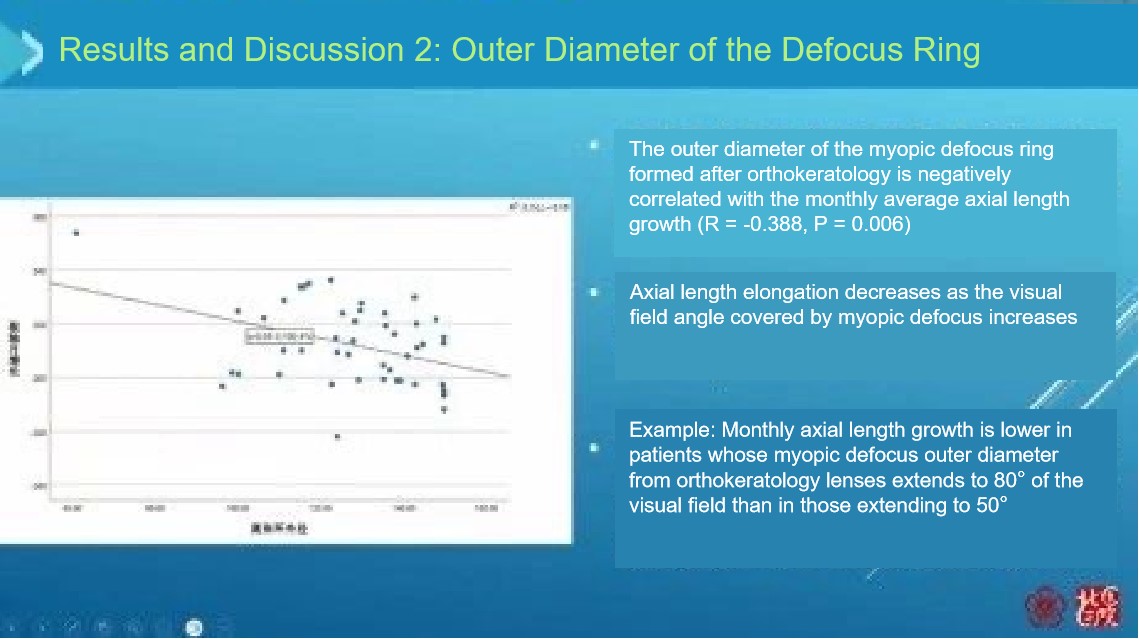
There is a negative correlation between the width and outer diameter of the defocus ring and axial elongation (the wider the width and the larger the outer diameter, the better the myopia control effect).

There is a positive correlation between the TRDV (Temporal Retinal Defocus Value) at a 53° visual field angle and the monthly average axial elongation (a smaller TRDV indicates a greater amount of myopic defocus, leading to a better myopia control effect).

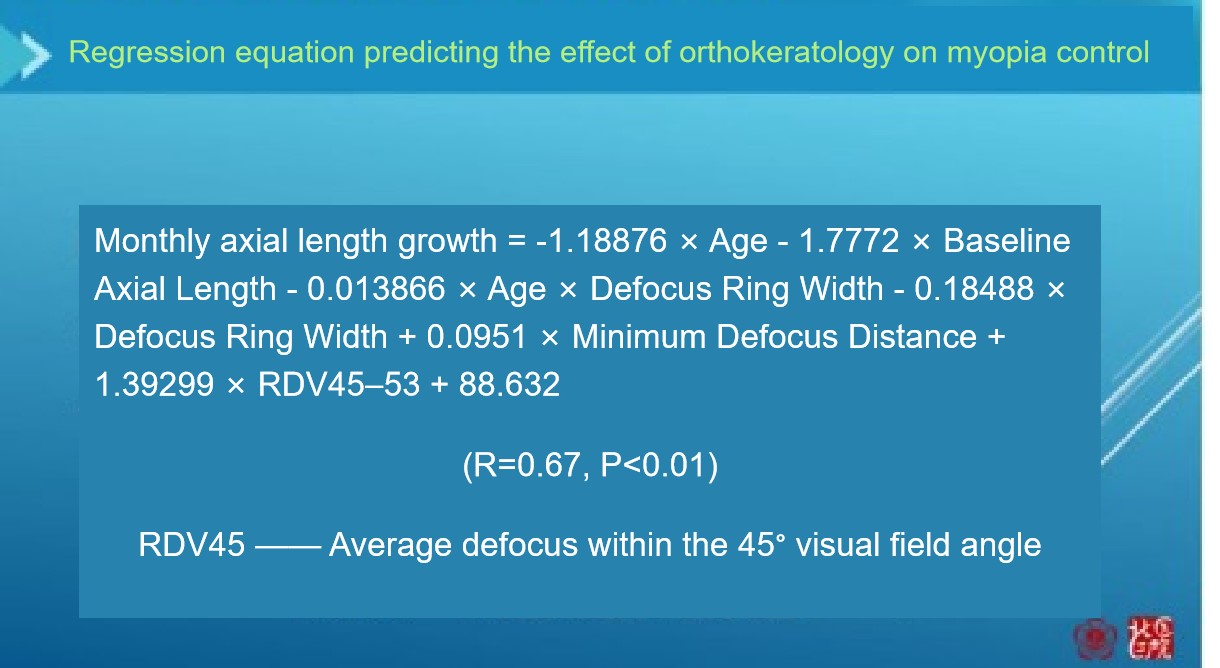
In addition, Professor Yu Zhang has innovatively constructed a multi-dimensional prediction model. By integrating patients’ age, baseline axial length, and MRT defocus parameters, this model can scientifically predict the axial elongation of myopic patients, providing a quantitative basis for formulating personalized intervention plans.

Finally, during the conference discussion session, experts conducted in-depth exchanges on the clinical translation of MRT technology and related hot topics. The content covered optimization strategies for orthokeratology (OK) lens design parameters, practical operation standards for MRT testing, and clinical considerations for decentered OK lenses, with the discussion lasting approximately 30 minutes.
Through the research sharing and in-depth discussions by authoritative experts, this session of the MRT Lecture Series has further clarified the core value of MRT technology in the clinical application of orthokeratology (OK) lenses — ranging from the quantification of defocus parameters and prediction of axial elongation to the optimization of personalized fitting and unification of clinical standards. It has established a key bridge for academic research and clinical practice in myopia prevention and control.
Recording Link of the Session:
https://meeting.tencent.com/crm/N88rQ8D58c
Shenzhen Thondar Technology Co., Ltd
Add: Floor 2, Building 13C, Zhonghaixin Innovation Industrial City, Longgang District, Shenzhen City, China 518112
Tel:+86-755-28377276
Fax:+86-755-84535972
Email: global@thondar.com



