Thondar Newsroom
On November 21, 2025, the 2nd Session of the MRT Lecture Series on Peripheral Refraction Assessment Technology was held as scheduled. This session specially invited Professor Fengju Zhang, Chief Optometrist at the Department of Medical Optometry, Beijing Tongren Hospital, and Deputy Head of the Ophthalmic Optics Group of the Chinese Ophthalmological Society, to deliver a keynote presentation on: “MRT Empowering Precision Myopia Control: Research on Peripheral Refraction Regulation in Children Using Defocus Soft Lenses.”
The seminar focused on core topics such as retinal defocus mechanisms, MRT detection technology applications, and defocus soft lens interventions, with in-depth discussions centered on practical clinical needs, offering new insights for precision myopia control.
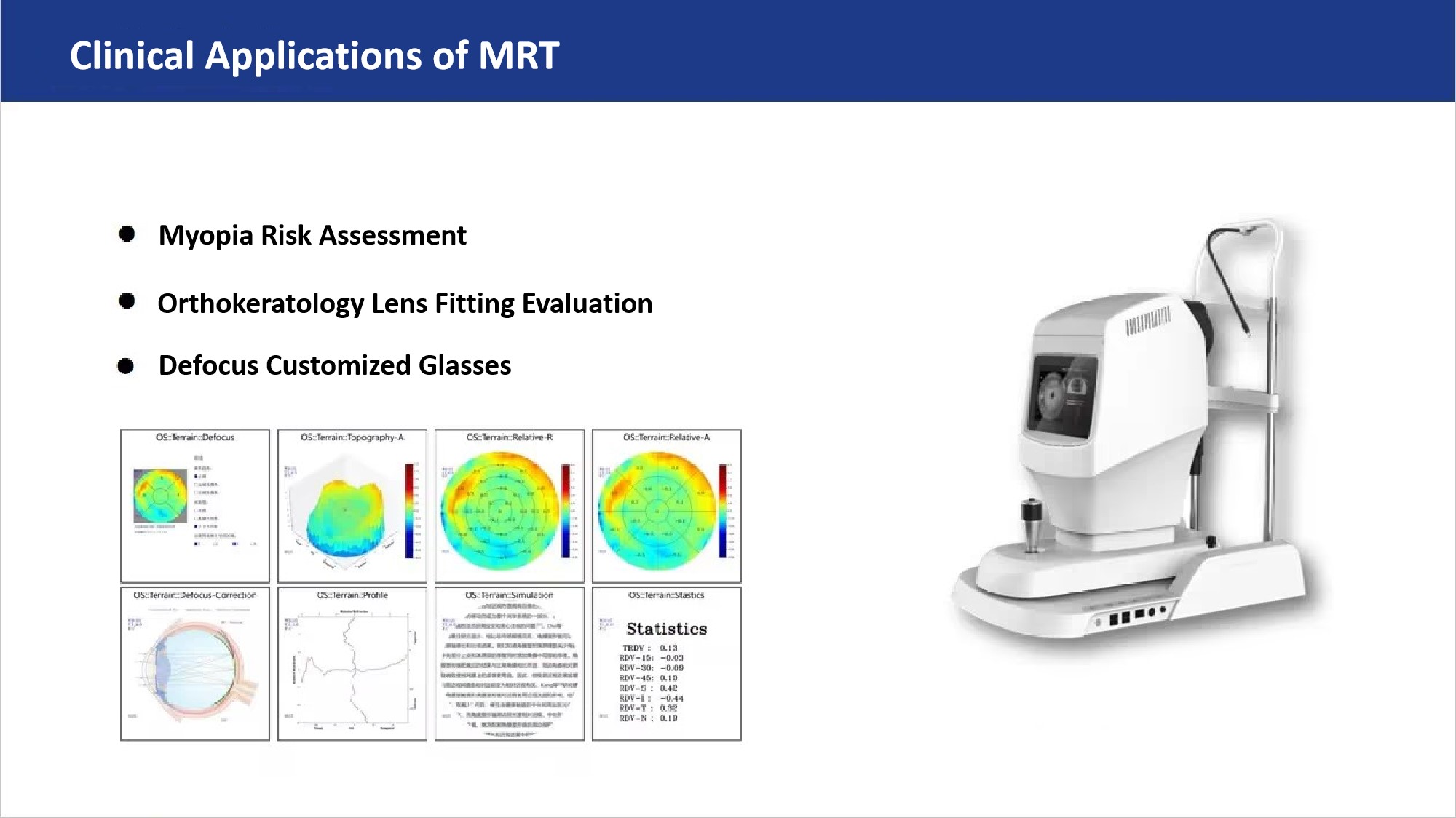
Professor Fengju Zhang pointed out that MRT technology, with its 53° wide-field detection advantage, enables precise quantification of peripheral refraction (RPR). Compared with traditional methods, MRT can capture the defocus status of different retinal regions in a single session, clearly presenting the defocus “differential” without being affected by ocular muscle contraction or accommodation, resulting in higher repeatability and accuracy. Whether for early defocus warning in children’s myopia, OK lens fitting evaluation, or customized defocus lens prescription, MRT provides critical data support.
Professor Zhang’s team conducted a prospective observational study involving 44 myopic children aged 7–16. Using MRT and OCTA, they tracked changes in peripheral refraction (RPR), retinal-choroidal vasculature, and axial length at 0, 3, 6, and 12 months after wearing MiSight contact lenses, aiming to clarify the relationship between RPR changes and myopia control outcomes.
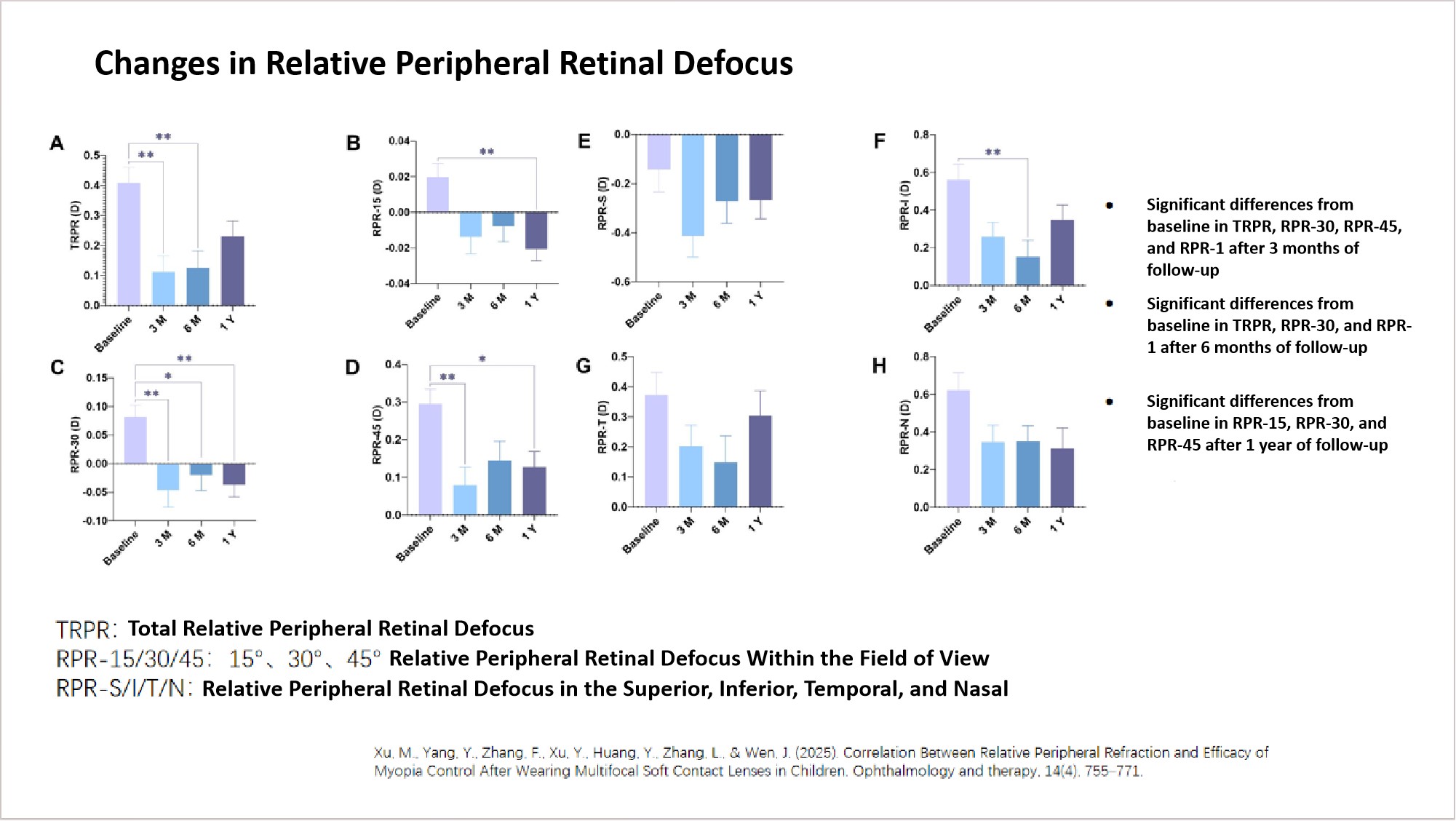
The results showed that after just 3 months of wearing MiSight contact lenses, multiple RPR indicators in children had significantly decreased, and these changes (ΔRPR) were negatively correlated with axial length growth rate. Among them, ΔTRPR and ΔRPR-45 showed the strongest correlation (r = -0.43). Changes in inferior and nasal retinal RPR also effectively reflected the trend of axial elongation, indicating that early RPR changes can predict myopia control outcomes.

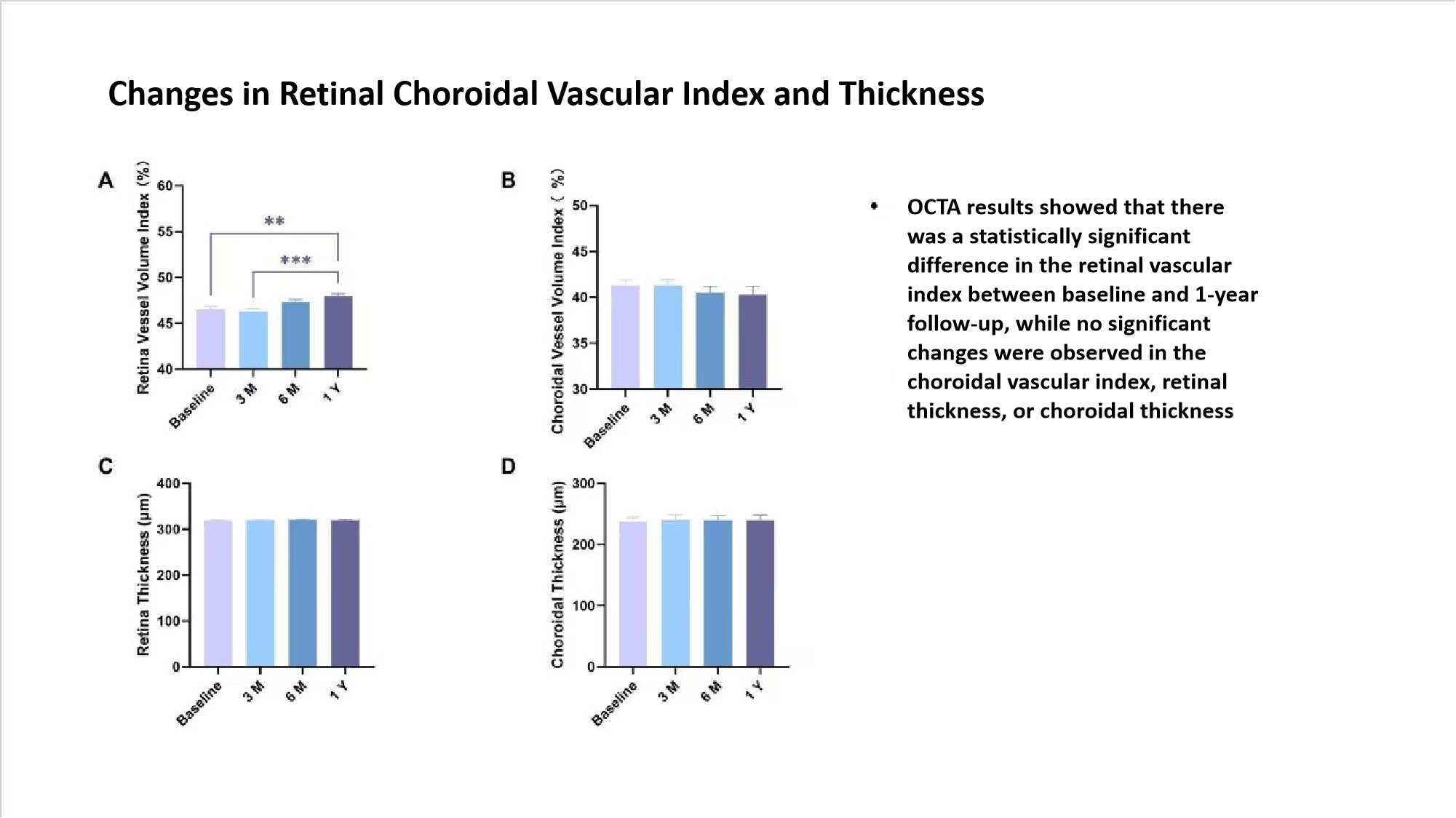
In contrast to the early response of RPR, significant changes in the retinal–choroidal vasculature were observed only after one year: the retinal vessel volume index (RVI) increased, while the choroidal vessel volume index (CVI), retinal thickness (RT), and choroidal thickness (ChT) showed no significant fluctuations. This suggests that retinal vascular changes may reflect a long-term mechanism of myopia control, whereas short-term assessments should focus more on RPR.
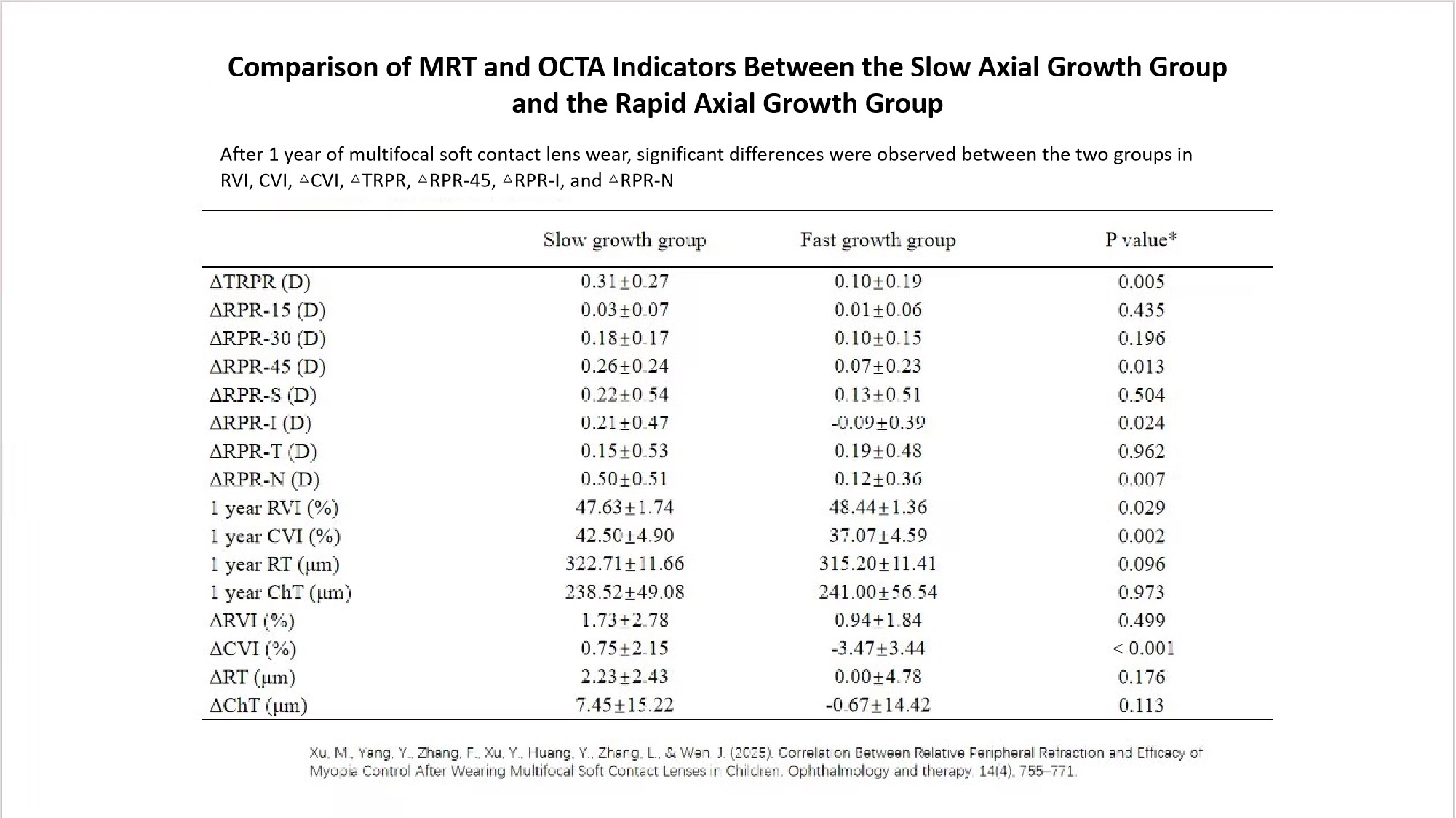
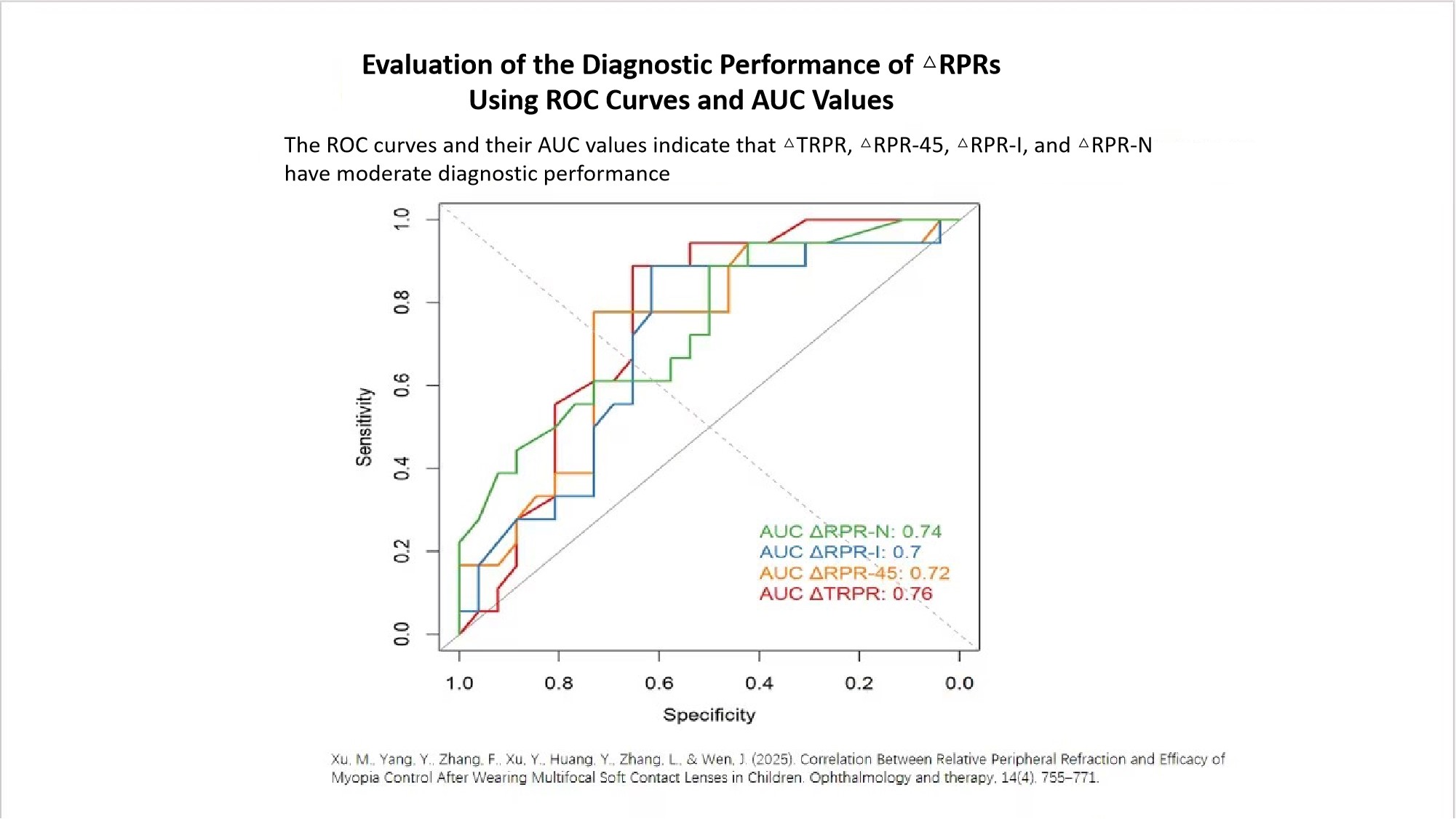
ROC curve analysis showed that the AUC values of ΔTRPR, ΔRPR-45, ΔRPR-I, and ΔRPR-N ranged from 0.70 to 0.76, indicating moderate diagnostic value. Among them, ΔTRPR had the highest AUC (0.76), making it a reliable indicator for predicting rapid axial elongation and providing a quantitative basis for identifying high-risk children and developing individualized intervention strategies.
During the discussion session, experts engaged in in-depth exchanges on topics such as the application of peripheral refraction in refractive surgery, its correlation with choroidal blood flow parameters, and practical procedures in defocus soft lens fitting, providing practical solutions for clinical technology implementation.
This session of the MRT Lecture Series, through multidimensional topic settings and exchanges of viewpoints, highlighted the core value of MRT in myopia control:
1. Defocus detection is the foundation of myopia control, and MRT provides critical support for precise quantification.
2. PRP is a reliable early indicator for predicting axial length growth.
3. MRT not only plays an important role in myopia risk assessment, contact lens fitting evaluation, and customized defocus lens prescription, but also holds promising applications in refractive surgery in the future.
Recording Link of the Session:
https://meeting.tencent.com/crm/Nx6oEgxm9a
Shenzhen Thondar Technology Co., Ltd
Add: Floor 2, Building 13C, Zhonghaixin Innovation Industrial City, Longgang District, Shenzhen City, China 518112
Tel:+86-755-28377276
Fax:+86-755-84535972
Email: global@thondar.com



