Thondar Newsroom
On December 3, 2025, At the 3rd MRT Lecture Hall · Seminar on Peripheral Refraction Detection Technology was successfully held. Professor Longqian Liu from West China Hospital of Sichuan University shared a series of the latest research findings and clearly pointed out: 1. The key to Orthokeratology lens in axial length control lies not in "the magnitude of defocus", but in "the position of defocus distribution"; 2. I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses: A two-year follow-up has confirmed a "72% sustained myopia progression slowing rate".
Professor Longqian Liu delivered a keynote report titled Both a Compass and a Navigator: Latest Research Progress of MRT in Orthokeratology lens Fitting and I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses. The seminar focused on the breakthrough research achievements of MRT in the fields of Orthokeratology lens and I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses, clarifying that MRT provides more accurate clinical evidence and practical approaches for adolescent myopia control.
01 MRT Reveals Key Changes in Peripheral Retinal Refraction After Orthokeratology Lens Treatment
In a study on "Characteristics of Peripheral Retinal Refraction Distribution and Its Correlation with Axial Length Growth", the results showed that:
(1) After orthokeratology lens treatment, the Relative Peripheral Refraction (RPR) in all quadrants shifted significantly toward the myopic direction, forming effective peripheral myopic defocus and thereby inhibiting axial length growth.
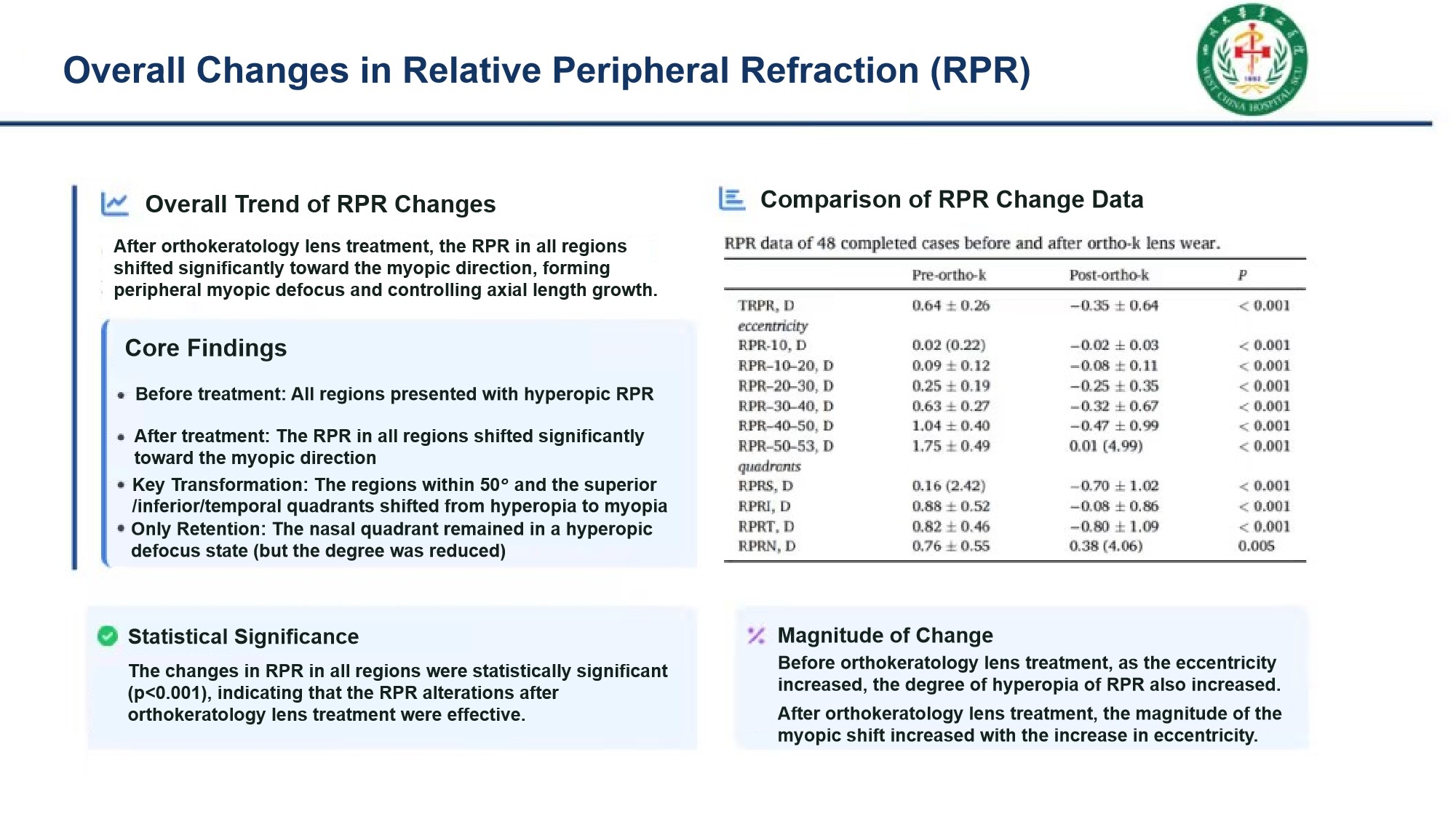
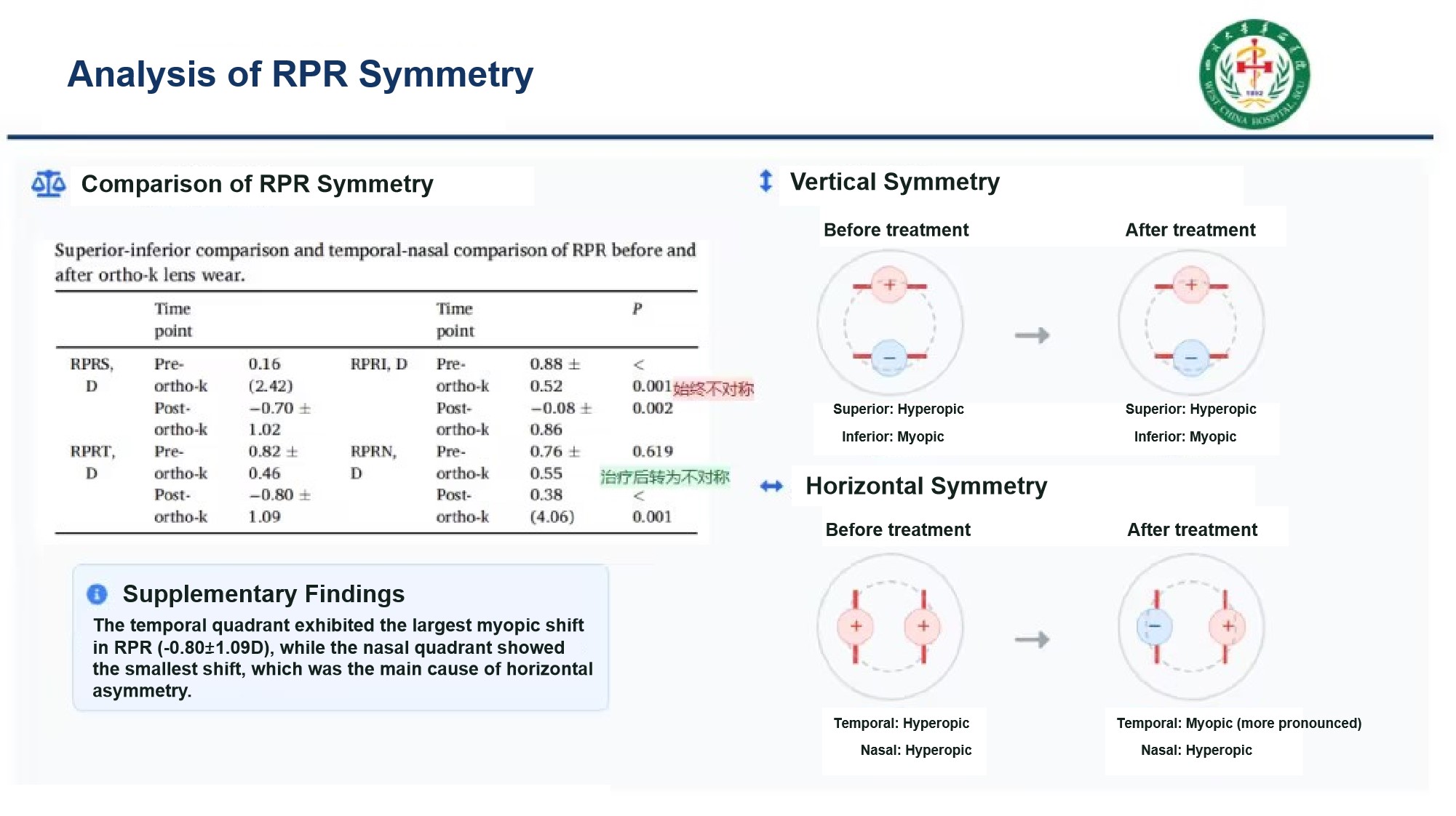
(2) The Relative Peripheral Refraction (RPR) in the vertical direction showed an asymmetric distribution both before and after treatment; while the RPR in the horizontal direction changed from a symmetric distribution before lens wear to an asymmetric distribution after lens wear.
(3) The more significant the myopic shift in the 30–40° region and the inferior quadrants, the more prominent the axial length control effect.
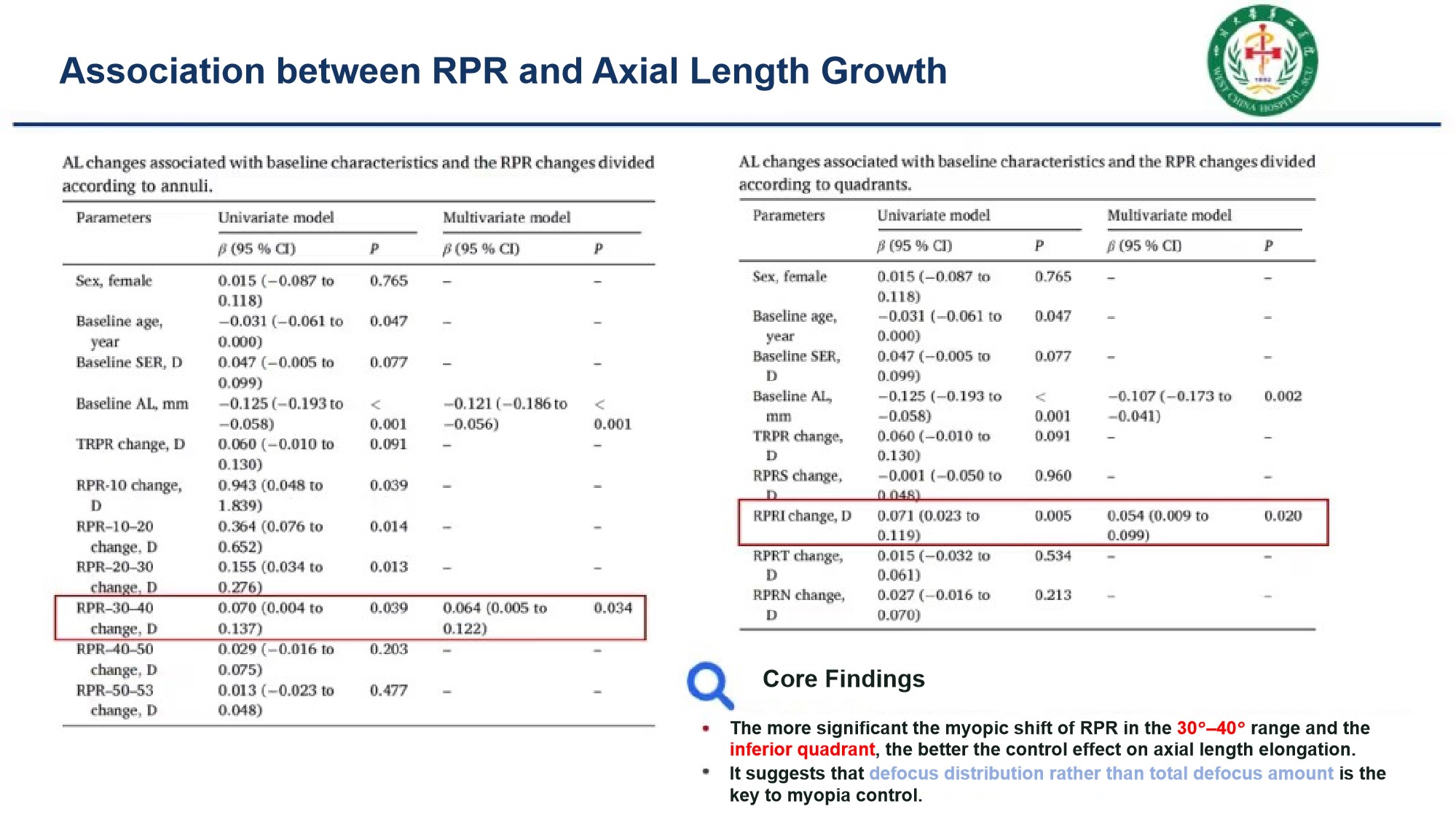
The factor determining axial length growth is not the "total amount of defocus", but the "spatial distribution characteristics of defocus in different retinal regions". This provides an important direction for the precise optimization of the reverse geometry design of orthokeratology lenses (such as peripheral curvature and positioning strategies).
02 I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses: Two-Year Follow-Up Confirms Sustained Efficacy
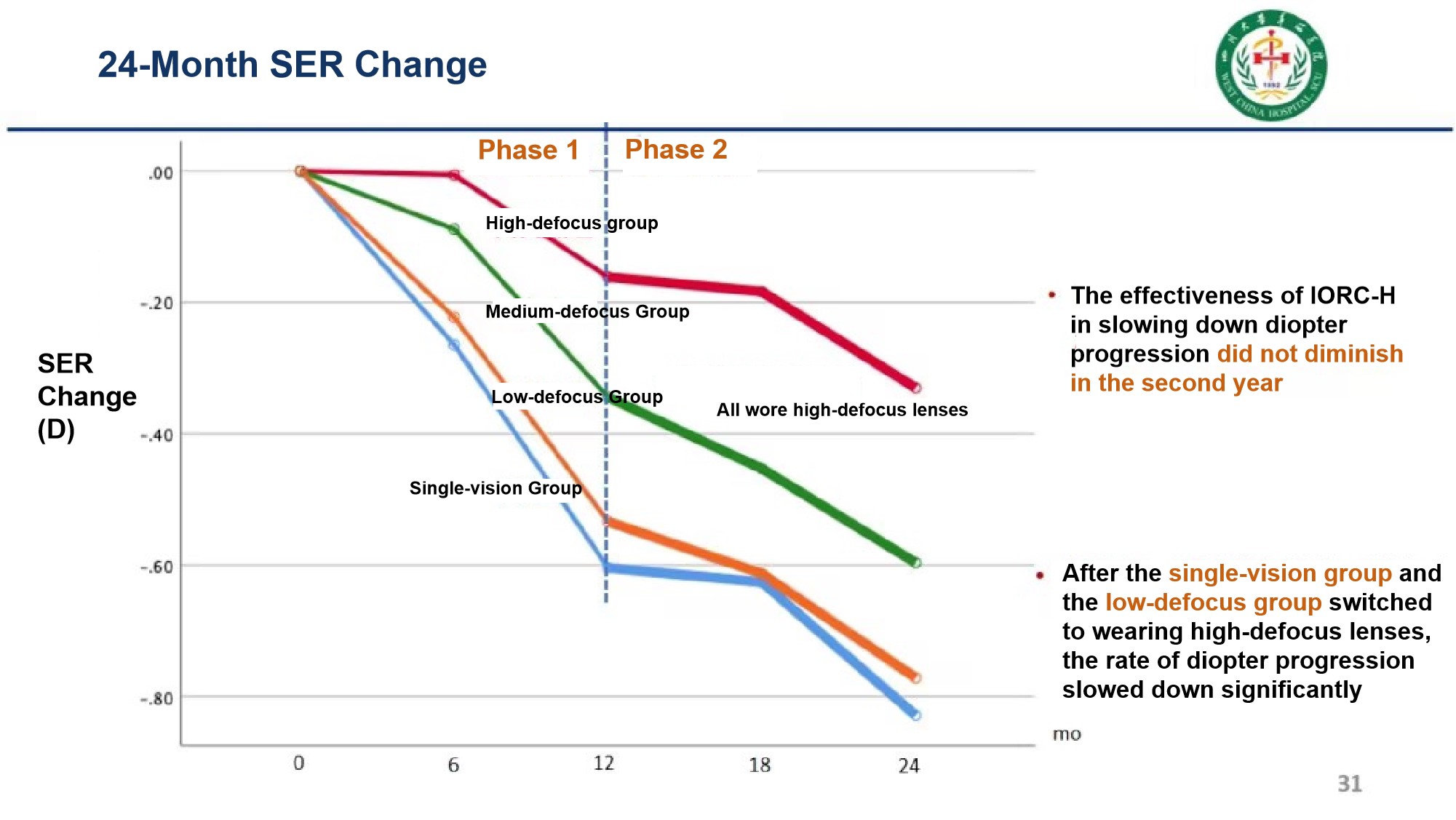
Another study on "Two-Year Clinical Efficacy Observation of I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses" showed that the equivalent diopter progression slowing rate of I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses reached 72% in both the first and second years, demonstrating sustained and stable myopia control efficacy.
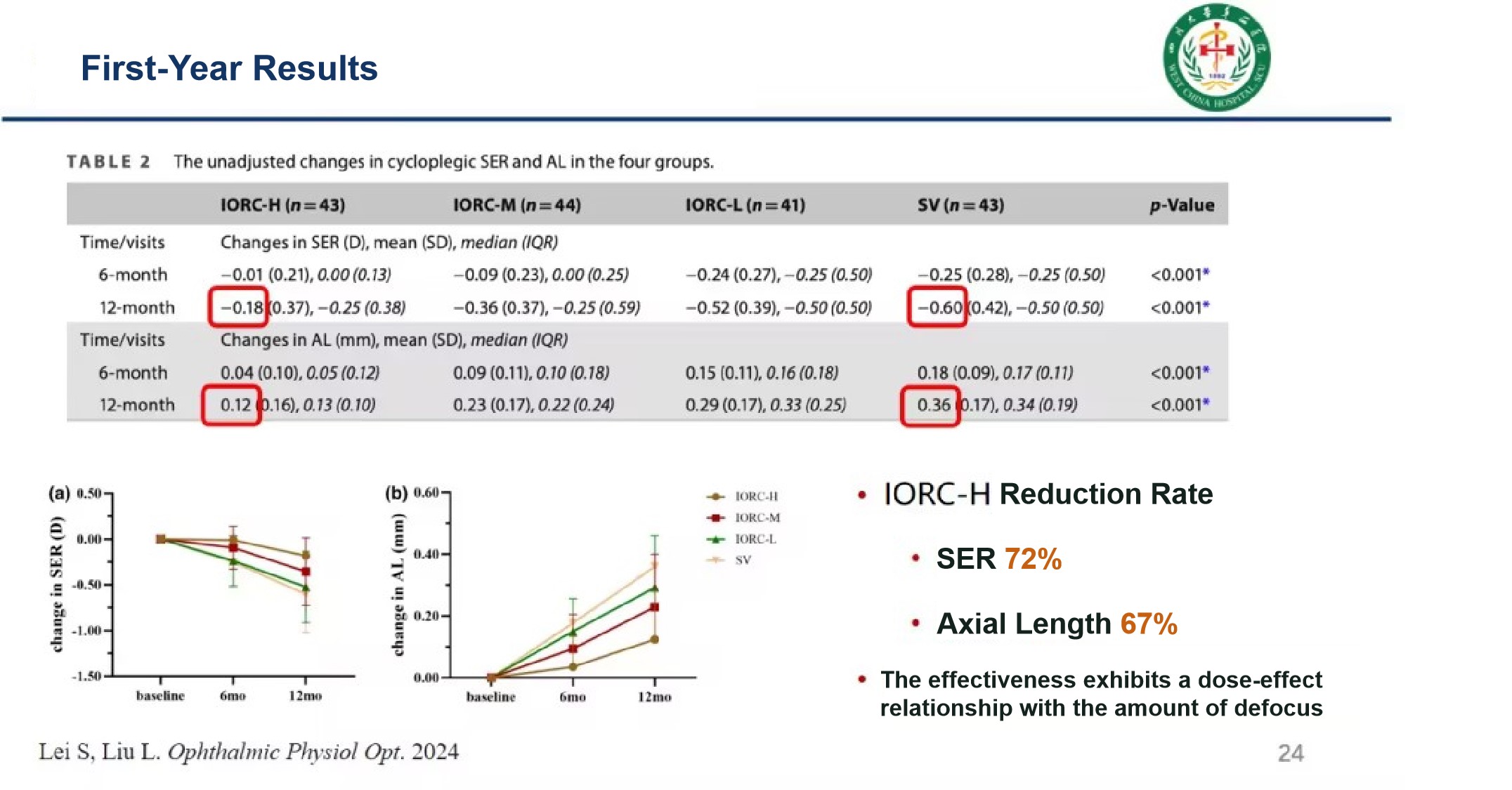
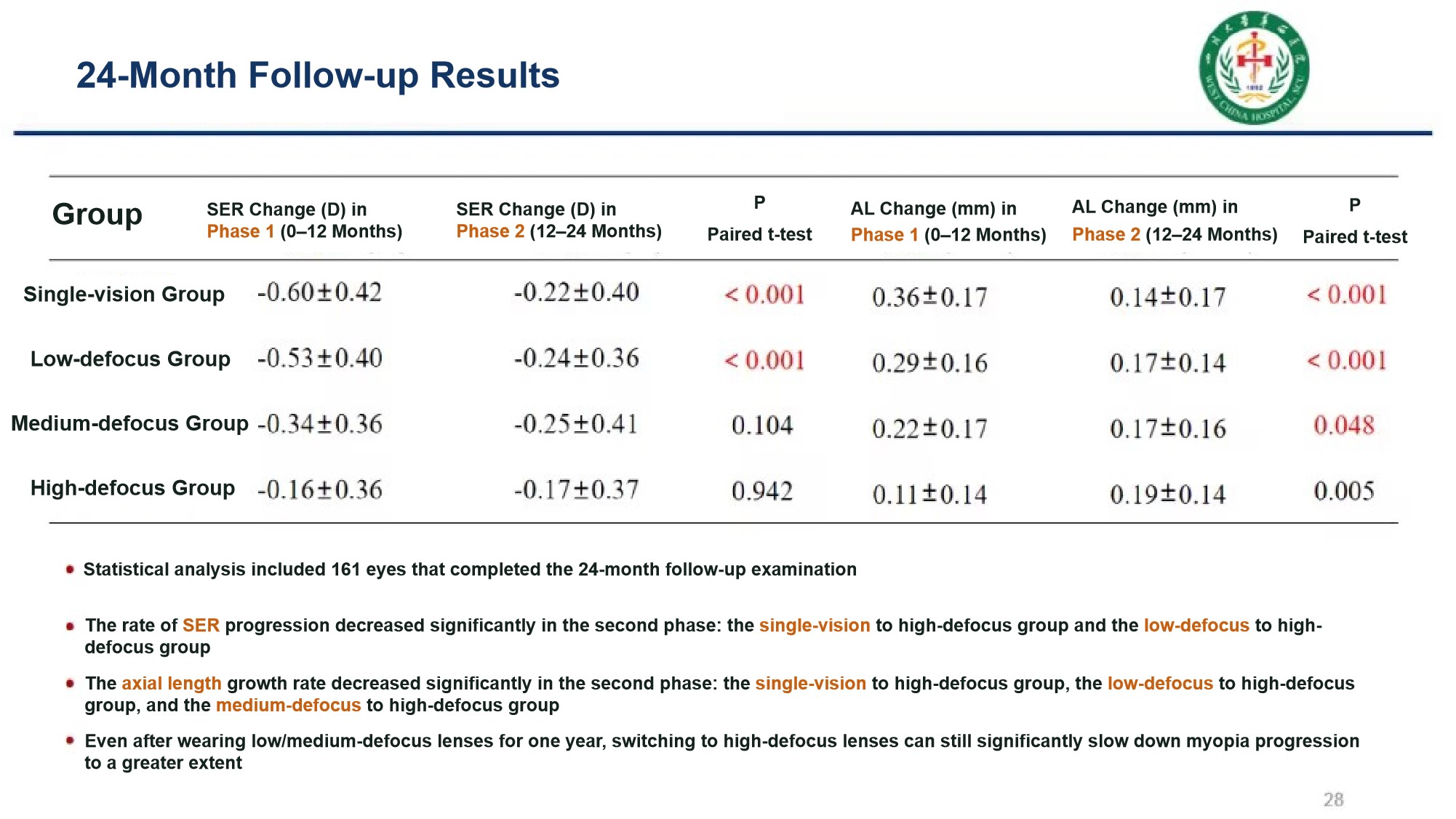
The study found that after switching from single-vision lenses or low/medium defocus lenses to customized lenses with high defocus power, the rate of myopia progression in children decreased significantly.

During the discussion session, participating experts conducted in-depth exchanges around core issues such as MRT application in fitting decision-making, interpretation of retinal defocus characteristics, and lens design optimization, and put forward a number of suggestions with practical guiding significance.
The following consensus was reached at this session:
1. Core Value of MRT in Myopia Control: The spatial distribution of Relative Peripheral Refraction (RPR) is a key parameter for regulating axial length growth, among which the 30–40° annulus and the inferior retinal quadrant are core targets for myopia control;
2. Orthokeratology lenses can directionally optimize defocus distribution by adjusting reverse geometry parameters to improve control efficacy;
3. I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses have maintained a 72% myopia progression slowing rate over two years, verifying their long-term intervention value, and more than 40 replication studies have been published so far;
4. I.O.R.C. Myopia lenses have performed particularly prominently in terms of spherical equivalent refraction control and axial length control.
Meeting recording link: https://meeting.tencent.com/crm/ldDkwR6Jbd
Shenzhen Thondar Technology Co., Ltd
Add: Floor 2, Building 13C, Zhonghaixin Innovation Industrial City, Longgang District, Shenzhen City, China 518112
Tel:+86-755-28377276
Fax:+86-755-84535972
Email: global@thondar.com



